
Basic electricity
Electricity produces three effects:
1. heat and light as in
a light bulb, electric fire or cooker;
2. magnetism as in an electromagnet;
3.
chemical changes as in electrolysis and electroplating.
Conductors
and insulators
A material which will allow electricity to flow through it is called a
CONDUCTOR and one which will not is called an INSULATOR.
All metals are
conductors, as are many liquids. Insulators are materials like plastics and
rubber.
Voltage and current
In Britain the mains voltage is 240 V; the
current taken from a socket depends on what you are using. Most plugs now have a 13 A
fuse but this maybe too large for some things and you should always
check.
The
plug
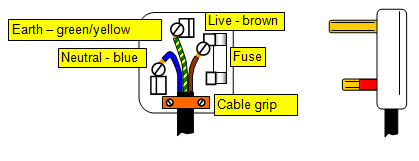
There are three wires to a modern 13 A plug:
1. live - coloured
brown
2. neutral - coloured blue
3. earth - coloured green/yellow stripes.
Earth
The earth wire is there to prevent the casing of
the equipment becoming live if something goes wrong. The electricity is conducted to earth,
usually via a metal water pipe.
Some things only have two wires with no earth, they have
plastic cases or cases made of other non-conducting material.
NEVER ALTER ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS AT HOME IF THEY ARE PART OF
THE MAINS.

Light bulbs
The filament in a light bulb is a coiled coil of
tungsten wire. The inside of the bulb is filled with argon or nitrogen and not air. The wire
glows white hot when a current flows through it. It does not catch fire because of the lack of
oxygen.
Switches
The purpose of a switch is fairly obvious
component but they too must be correctly connected. You must always connect a switch in
the live wire so that the socket/appliance is not live when it is switched
off.

Fuses
A fuse is usually a thin piece
of wire that will melt and break the circuit if too large a current flows through it. The thicker
the wire the more current is needed to melt it and the higher the 'rating' of the fuse. The purpose of a fuse is to protect the wiring
and the equipment. If the fuse was not there and something went wrong then the wires
themselves would get hot and maybe catch fire. In a plug the fuse is in a glass
tube.
Fuses should also be connected in the live wire you should always switch off
before changing a fuse.
The normal fuse ratings are 13 A, 5 A, 3 A and 1 A. Currents
bigger than these will 'blow' the fuse.
Circuit breakers
In
houses today most fuse boxes are being replaced by a set of switches called circuit
breakers. These act a bit like a fuse, cutting off the supply if there is a problem. However they
are based on an electronic circuit and are safer than fuses because they act to cut off the
current much more quickly.
Direct current (d.c) and Alternating current
(a.c)
There are two 'types 'of electricity depending on how they were
produced.
Direct current - or d.c. This means current that is always flowing in the
same direction, and is taken to be from positive to negative; d.c. is made by a battery or a
d.c. generator.
Alternating current - or a.c. This means current that is constantly
changing direction, first flowing one way and then the other. In Britain a complete cycle takes
one fiftieth of a second - the frequency of the mains is 50 Hz.
You can see how the
voltage of d.c. and a.c. changes with time if you connect them to an oscilloscope.

A VERSION IN WORD IS AVAILABLE ON THE SCHOOLPHYSICS USB


 There are three wires to a modern 13 A plug:
There are three wires to a modern 13 A plug:


